[TIME STAMP]: [Visual Description]
[VO]
[Caption]
[Legal Super]
[00:00 – 00:05] [EBGLYSS logo, Indication, Select Important Safety Information and Please See line]
[N/A]
[INDICATION
EBGLYSS™ (lebrikizumab-lbkz) is indicated for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older who weigh at least 40 kg with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. EBGLYSS can be used with or without topical corticosteroids.
Select Important Safety Information
CONTRAINDICATION: EBGLYSS is contraindicated in patients with prior serious hypersensitivity to lebrikizumab-lbkz or any excipients of EBGLYSS.
Please see accompanying Prescribing Information and Patient Information.
Please see Instructions for Use included with the device.]
[00:07 – 00:12] [Open on an undulating waveform. The waves spike as we slowly push in.]
[Hear that? That’s the sound of disruption from AD.]
[00:13 – 00:18] [A hand rises up through the waves. Second hand rises up through the waves.]
[AD, or atopic dermatitis, is primarily an IL-13 dominant disease.]
[IL=interleukin.]
[00:19 – 00:23] [One hand begins scratching the other. The first arm develops a glowing inflamed area to match with “pro-inflammatory role” in VO.]
[IL-13 is a cytokine with a pro-inflammatory role in the skin.]
[IL=interleukin.]
[00:24 – 00:27] [Camera movement takes the viewer around the hands.]
[IL-13 is elevated in non-lesional and lesional skin,…]
[00:28 – 00:31] [The hands continue scratching. Camera travels past the scratching hands.]
[…which can cause disruptive symptoms for patients with AD.]
[00:32 – 00:35] [Camera moved through the waves.]
[IL-13 levels correlate with disease severity and chronicity–…]
[00:36 – 00:37] [Camera pans wide to woman scratching her neck.]
[…the noise from AD…]
[00:38 – 00:42] [Camera zooms closer to woman as her skin glows, representing inflammation.]
[…and IL-13 has direct effects on itch and pruritogen sensitization,…]
[00:43 – 00:47] [As the camera moves around, it seems as though the waves are emanating from the inflamed areas. We continue orbiting around her as she scratches another region on her elbow.]
[…indicating that IL-13 is a therapeutic target for patients with AD.]
[00:48 – 00:51] [We continue to follow the lines away from the center of the action. Pull back as we begin our transition. Pull back further to reveal the sound line transitioning. The wave line collapses down into a point; that point becoming the red jewel shape (IL-13) that represents the inflammation.]
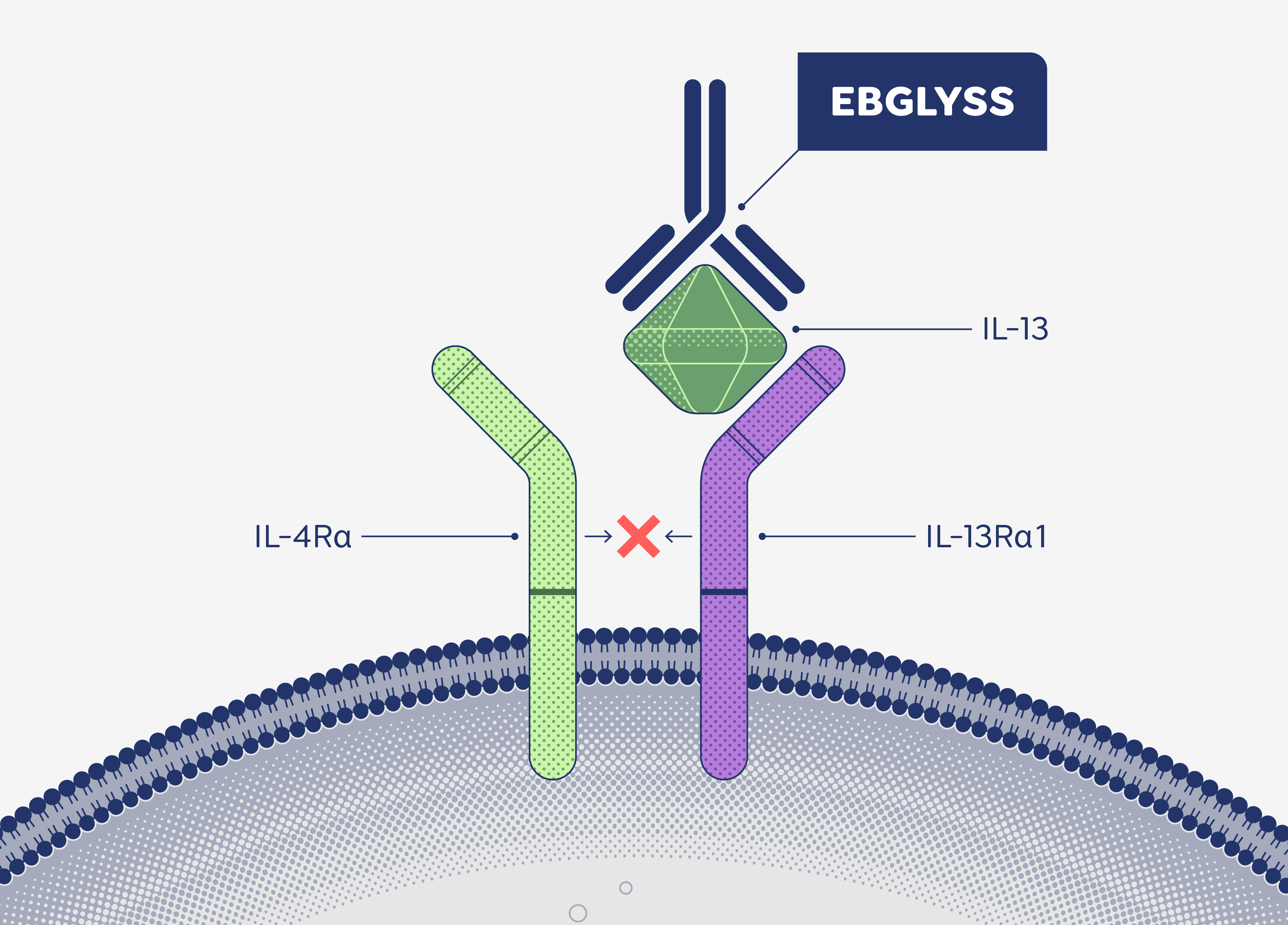
[IL-13 signaling occurs through a receptor complex…]
[00:52 – 00:55] [The IL-13 cytokine floats down and finds the beginning of our MOA. We introduce the receptor complex of IL-13R⍺1 and IL-4R⍺.]
[…consisting of IL-13 receptor alpha 1 and IL-4 receptor alpha.]
[R⍺=receptor, alpha.]
[00:56 – 01:00] [IL-13 binds to IL-13R⍺1.]
[IL-13 initially binds to the IL-13 receptor alpha 1 subunit,…]
[R⍺=receptor, alpha.]
[01:01 – 01:04] [IL-4Rα rises up and joins the IL-13 + IL-13R⍺ unit.]
[…and then IL-4 receptor alpha is recruited.]
[01:05 – 01:06] [The complex is complete and starts to glow.]
[Intracellular transduction occurs through…]
[01:07 – 01:08] [We see the JAK-STAT pathway begin to activate, sending a signal to the nucleus of the cell.]
[…the activation of the JAK-STAT pathway.]
[JAK=Janus kinase;
STAT=signal transducer and activator of transcription.]
[01:09 – 01:11] [We start to zoom out from the cell]
[Can targeted action against this cytokine…]
[01:12 – 01:14] [Camera continues to pan away from the cell.]
[…play an important role in the treatment of AD?]
[01:15 – 01:18] [We pan up from the cells to find the EBGLYSS antibody alone. Dramatic movement of EBGLYSS traveling toward a glowing IL-13 cytokine.]
[EBGLYSS is a monoclonal antibody that selectively targets…]
[01:19 – 01:24] [EBGLYSS binds to IL-13. Pull back wider to show the unit of EBGLYSS and IL-13 binding to IL-13Rα .]
[…and neutralizes IL-13 with high binding affinity and a slow dissociation rate.]
[01:25 – 01:27] [As IL-13 binds to IL-13Rα1,…]
[EBGLYSS binds to the IL-13 cytokine…]
[01:28 – 01:29] […we see a sparkle as a signal of the connectivity.]
[…at an area that overlaps with the binding site…]
[01:30 – 01:32] [IL-4R⍺ tries to join IL-13Rα1,...]
[…of the IL-4 receptor alpha subunit of the…]
[01:33 – 01:37] […but is unable to form the receptor complex due to the presence of EBGLYSS.]
[IL-13 receptor alpha 1, IL-4 receptor alpha heterodimer,…]
[01:38 – 01:42] [Wide shot showing prevention of the full receptor complex and lack of signaling to the nucleus.]
[…preventing formation of this receptor complex and inhibiting IL-13 signaling.]
[01:43 – 01:46] [We float up…]
[IL-13 is implicated as a primary cytokine tied to…]
[01:47 – 01:53] [and pan off the scene. EBGLYSS flies into frame with an IL-13 cytokine.]
[…the pathophysiology of AD, and EBGLYSS selectively targets IL-13.]
[01:53 – 01:57] [EBGLYSS centers itself in-frame as we fade to safety.]
[EBGLYSS. Experience the potential of a targeted AD therapy.]
[01:58 – 04:49] [Scrolling indication & Important Safety Information]
[INDICATION
EBGLYSS™ (lebrikizumab-lbkz) is indicated for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older who weigh at least 40 kg with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. EBGLYSS can be used with or without topical corticosteroids.
Important Safety Information
CONTRAINDICATION: EBGLYSS is contraindicated in patients with prior serious hypersensitivity to lebrikizumab-lbkz or any excipients of EBGLYSS.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
HYPERSENSITIVITY
Hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema and urticaria, have been reported with use of EBGLYSS. If a serious hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue EBGLYSS and institute appropriate therapy.
CONJUNCTIVITIS AND KERATITIS
Conjunctivitis and keratitis adverse reactions have been reported in clinical trials. Conjunctivitis and keratitis occurred more frequently in atopic dermatitis subjects who received EBGLYSS compared to those who received placebo. Conjunctivitis was the most frequently reported eye disorder. Most subjects with conjunctivitis or keratitis recovered during the treatment period. Advise patients to report new onset or worsening eye symptoms to their healthcare provider.
PARASITIC (HELMINTH) INFECTIONS
Patients with known helminth infections were excluded from participation in clinical studies. It is unknown if EBGLYSS will influence the immune response against helminth infections by inhibiting IL-13 signaling. Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating treatment with EBGLYSS. If patients become infected while receiving EBGLYSS and do not respond to antihelminth treatment, discontinue treatment with EBGLYSS until the infection resolves.
VACCINATIONS
EBGLYSS may alter a patient’s immunity and increase the risk of infection following administration of live vaccines. Prior to therapy with EBGLYSS, complete all age-appropriate vaccinations according to current immunization guidelines. Avoid use of live vaccines immediately prior to or during treatment with EBGLYSS. No data are available on the response to live vaccines.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common (≥1%) adverse reactions are conjunctivitis, injection site reactions, and herpes zoster.
EBGLYSS is available as a 250mg/2mL subcutaneous injection prefilled pen or prefilled syringe.
Please see accompanying Prescribing Information and Patient Information.
Please see Instructions for Use included with the device.]
LK HCP ISI AD APP
[04:50 – 04:56] [Indication and ISI fade out and video references appear.]
[N/A]
[References
- Bieber T. Interleukin-13: targeting an underestimated cytokine in atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2020;75(1):54-62. doi:10.1111/all.13954
- EBGLYSS (lebrikizumab-Ibkz). Prescribing Information. Lilly USA, LLC.
- Gittler JK, Shemer A, Suárez-Fariñas M, et al. Progressive activation of TH2/TH22 cytokines and selective epidermal proteins characterizes acute and chronic atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130(6):1344-1354. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.012
- Gonçalves F, Freitas E, Torres T. Selective IL-13 inhibitors for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Drugs Context. 2021;10:2021-1-7. doi:10.7573/dic.2021-1-7
- La Grutta S, Richiusa P, Pizzolanti G, et al. CD4+IL-13+ cells in peripheral blood well correlates with the severity of atopic dermatitis in children. Allergy. 2005;60(3):391-395. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2005.00733.x
- McCormick SM, Heller NM. Commentary: IL-4 and IL-13 receptors and signaling. Cytokine. 2015;75(1):38-50. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.023
- Miron Y, Miller PE, Hughes C, et al. Mechanistic insights into the antipruritic effects of lebrikizumab, an anti-IL-13 mAb. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;150(3):690-700. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.01.028
- Okragly AJ, Ryuzoji A, Wulur I, et al. Binding, neutralization and internalization of the interleukin-13 antibody, lebrikizumab. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). Published online June 13, 2023. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00947-7
- Ratnarajah K, Le M, Muntyanu A, et al. Inhibition of Il-13: a new pathway for atopic dermatitis. J Cutan Med Surg. 2021;25(3):315-328. doi:10.1177/1203475420982553
- Suárez-Fariñas M, Tintle SJ, Shemer A, et al. Nonlesional atopic dermatitis skin is characterized by broad terminal differentiation defects and variable immune abnormalities. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(4):954-964. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2010.12.1124
- Tsoi LC, Rodriguez E, Degenhardt F, et al. Atopic dermatitis is an IL-13-dominant disease with greater molecular heterogeneity compared to psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139(7):1480-1489. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2018.12.018
- Ultsch M, Bevers J, Nakamura G, et al. Structural basis of signaling blockade by anti-IL-13 antibody lebrikizumab. J Mol Biol. 2013;425(8):1330-1339. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2013.01.024]
[04:57 – 04:59] [EBGLYSS waves animate on-screen.]
[EBGLYSS AUDIO SIGNATURE BEGINS]
[N/A]
[05:00 – 05:06] [Logo and end matter appear on screen.]
[EBGLYSS AUDIO SIGNATURE CONCLUDES]
[[EBGLYSS logo]
Ebglyss™
(lebrikizumab-lbkz)
250mg/2mL injection
PP-LK-US-0195 09/2024 © Lilly USA, LLC 2024. All rights reserved.
EBGLYSS™ and its delivery device base are trademarks owned or licensed by Eli Lilly and Company, its subsidiaries, or affiliates.
[Eli Lilly logo]]